Near-Infrared Fluorescent EMSA Kit and Oligonucleotides
Products
Mobility shift assay protocols can be easily converted to infrared fluorescent assays by replacing the existing DNA oligonucleotides with IRDye® infrared dye end-labeled oligonucleotides. Binding and electrophoresis conditions are the same as any other EMSA detection method.
A DNA oligonucleotide end-labeled with IRDye 700 infrared dye is a good substrate for protein binding. Using the Odyssey® Infrared Imaging System, IRDye infrared dye labeled DNA detection is linear within a 50-fold dilution range from 9.1 fmol to 0.18 fmol.
Perform NIR Fluorescent EMSA and Save Time
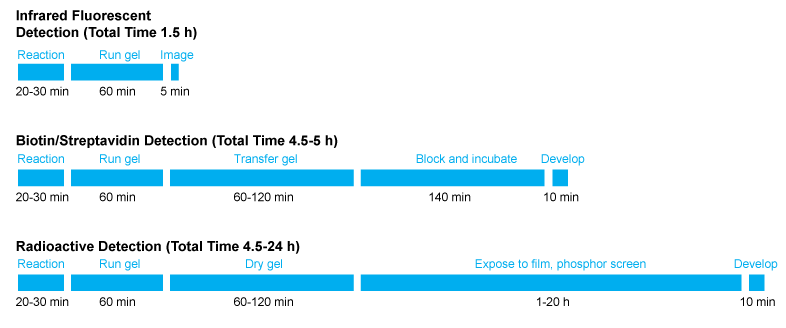
Infrared fluorescent assays can be completed in less than two hours with no gel transfer or film exposure. The gel doesn’t even have to be removed from the glass plates for imaging. If you are not satisfied that the electrophoresis has progressed far enough, you can place the gel back into the electrophoresis unit and run longer.
Other IRDye 700 oligonucleotides as well as IRDye 800 oligonucleotides are available through Integrated DNA Technologies, TriLink BioTechnologies, or Metabion International AG.
Near-Infrared Fluorescence Detection for Gel Shift Assays Has Advantages over Use of Radioisotopes
| Infrared | Radioisotope |
|---|---|
| Easy access and disposal | Short half-life of the label |
| Dye is stable for a long time | Regulatory procedures Disposal limitations |
| Non-hazardous | Hazardous |
| Gel (glass plates) can be easily imaged on the Odyssey | Lengthy incubations with autoradiographic film |
| Detection of the probe is rapid | Time-consuming and inconvenient |
| Gel can be replaced back and run longer | Not possible |


