IRDye 800CW 2-DG (2-deoxyglucose) is a fluorescent optical imaging agent that has been shown to be reactive with implanted tumors derived from many cell lines including A431, SW620, 3T3-L1, and PC3LMN4. This optical imaging agent has been used for numerous applications, including research pertaining to tumor biology, tumor metastases, diabetes, and arthritis.
Cancer cells are often characterized by a high metabolic rate exemplified by an elevated rate of glycolysis. This observation forms the basis for positron emission tomography (PET) using glucose analogues such as 18F-2-deoxy-D-glucose (18FDG) to visualize primary tumors and their metastasis. Radiolabeled 2-deoxy-D-glucose (2-DG) is generally impractical for use in small animal studies of cancer biology. Fluorophore-labeled variants of 2-deoxy-D-glucose have been used with varying degrees of success.1, 2, 3
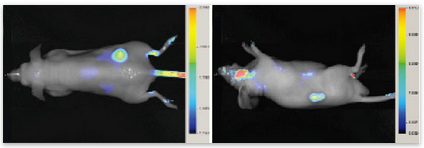
The optical agent exhibits the expected dose response with increasing concentrations of the agent in both cell based and animal experiments. Uptake of the agent can be effectively blocked with either unlabeled 2-DG or glucose, confirming its specificity.
Confocal microscopy demonstrated conclusively that IRDye 800CW 2-DG is taken up by the cell and localized in the cytoplasm. While the exact mechanism of IRDye 800CW 2-DG uptake is not known, there is strong evidence for the involvement of the GLUT transporter system.
Learn about other LI-COR optical probes.
Applications
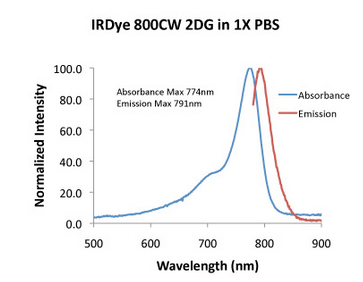
Absorbance and Emission Spectra
Data Example
References
- Lloyd, P.G., Hardin, C.D., and Sturek, M. (1999). Physiol Res, 48. 401-10.
- O'Neil, R.G., Wu, L., and Mullani, N. (2005) Mol Imaging Biol, 7. 388-92.
- Cheng, Z., Levi, J., Xiong, Z., Gheysens, O., Keren, S., Chen, X., and Gambhir, S.S. (2006) Bioconjug Chem, 17. 662-9.
- Kovar, J. L., Volcheck, W. M., Sevick-muraca, E., Simpson, M. A., & Olive, D. M. (2009). Anal Biochem, 384(2). 254-262. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2008.09.050.
